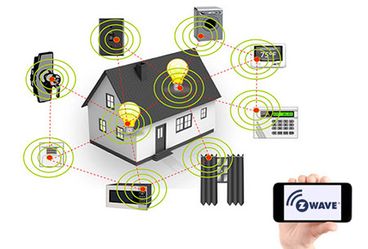
About Z-Wave technology
Z-Wave is a wireless communications protocol used primarily for home automation. Z-Wave is based on a mesh network topology. This means each (non-battery) device installed in the network becomes a signal repeater. As a result, the more devices you have in your home, the stronger the network becomes.
Z-Wave’s devices can communicate point-to-point for up to 120 feet on their own, but with their ability to hop signals, effective ranges of up to 600 feet are easily achieved, and Z-Wave networks can be linked together for even larger deployments. Each Z-Wave network can support up to 232 Z-Wave devices allowing you the flexibility to add as many devices as you’d like to make sure your Smart Home is working it’s hardest.
Z-Wave Technology Essentials:
- Low Powered RF communications technology that supports full mesh networks without the need for a coordinator node
- Operates in the sub-1GHz band; impervious to interference from Wi-Fi and other wireless technologies in the 2.4-GHz range (Bluetooth, ZigBee, etc.)
- Designed specifically for control and status apps, supports data rates of up to 100kbps, with AES128 encryption, IPV6, and multi-channel operation
- Full interoperability through layer 6 with backwards compatibility to all versions.
- Successfully bridged and trialed with OpenADR, SEP 1, SEP 1.1 and other Smart Energy protocols.
- Shares the same position in the NIST / SGIP Catalog of Standards as the IEEE 802.11 and 802.15 and 802.16 families
Z-Wave Market Facts:
- Over 2100 interoperable products available, 70 million Z-Wave products worldwide.
- Actively supported by over 600 manufacturers and service providers throughout the world.
- Designed specifically for control, monitoring and status operations; no interference from Wi-Fi or other 2.4GHz wireless technologies in similar band.
References
Related articles
Copyright © Animus Home